Introduction to Multiphase Flows
Appendix 1
A1.1 Conservation Equations for “Closed Systems”
- In Thermodynamics, System = Mass
- Closed system No mass exchange
Conservation laws can be written for a closed system and constitute the basis for the solution of all thermodynamics, mechanics, and what engineers call “thermal-hydraulics” problems (combination of heat transfer and fluid mechanics or hydraulics).
- The three fundamental conservation laws:
- Conservation of Mass
- Eg: Deformation of a baloon (change in volume, mass is same)
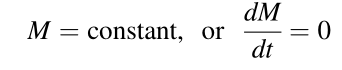
- Conservation of Momentum (Newton’s law of motion)
- Sum of all forces applied on a body equals the rate of change of momentum in that body
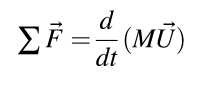
- Conservation of Energy (First Law of Thermodynamics)
- Heat added to the system minus work done by the system equals change in the internal energy
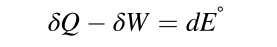
- indicates that is a thermodynamic Property
Chapter 1: Nature of Multiphase Flows and Basic Concepts
Multiphase Flow: It is the flow of materials with two or more phases. Eg. oil-water mixture, slurry etc.
Phenomena Unique to Multiphase flow
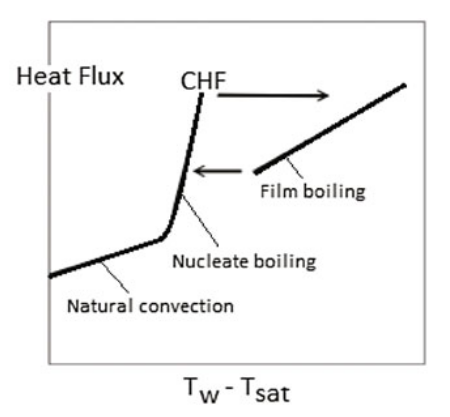
Critical Heat Flux (CHF)
In a Pool Boiling case where & are Wall and saturation temperatures.
When the difference between water and the Wall reaches CHF, the heat disparity rapidly increases as there is very little cooling of the wall as the water has changed to vapor and the heat transfer & density of Steam is less compared to water. Because there is no cooling, the Wall may fail.
First reported by Nukiyama’s Boiling curve.1
References
Yadigaroglu, G., & Hewitt, G. F. (2018). Introduction to multiphase flow: Basic concepts, applications and modelling. Cham: Springer
Footnotes
-
Nukiyama S (1934) The maximum and minimum value of the heat transmitted from metal to boiling water under atmospheric pressure. J Japan Soc of Mech Engrs 37: 367–374. See also translation in Int J Heat Mass Transfer (1966) 9:1419-1433 ↩