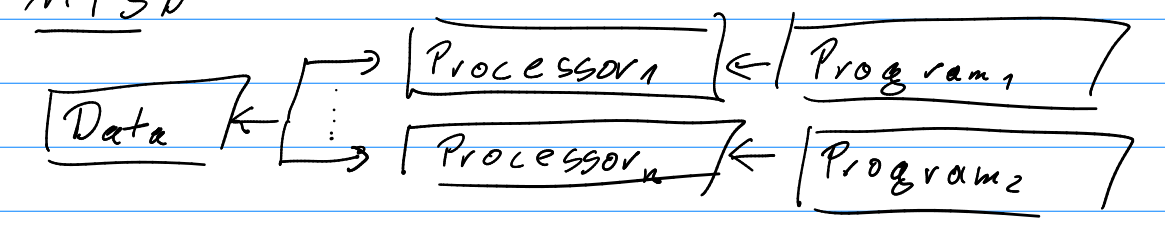Background
- Data Starvation Crisis: Processing improves much faster than Memory Avancements.
- Hardware layout plays a big rule in the effectiveness of Parallel Computing.
Machine Classification by Flynn
graph TD;
A[Machine Architecture Classification]
A --> B[SISD]
A --> C[MISD]
A --> D[SIMD]
A --> E[MIMD]
- Single Instruction Single Data (SISD)
- Single Core machine
- Sequential Programming

- Multiple Instruction Single Data (MISD)
- Data←>Multiple Processors←Multiple Programs
- Not used for Scientific computing
- Used for redundancy.
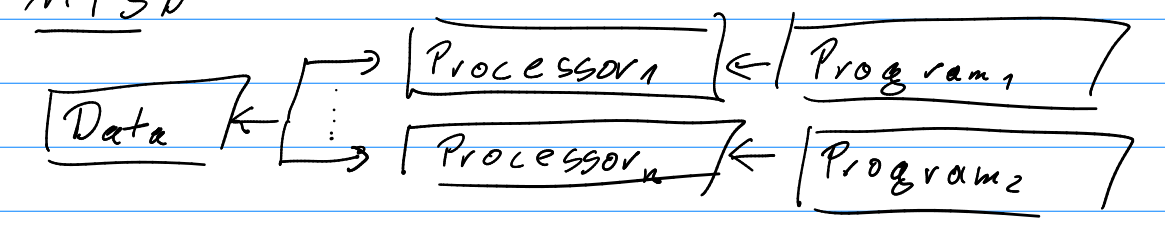
- Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD)
- Multiple Data←>multiple processors←single program
- vector architectures eg: gpus, vector units.

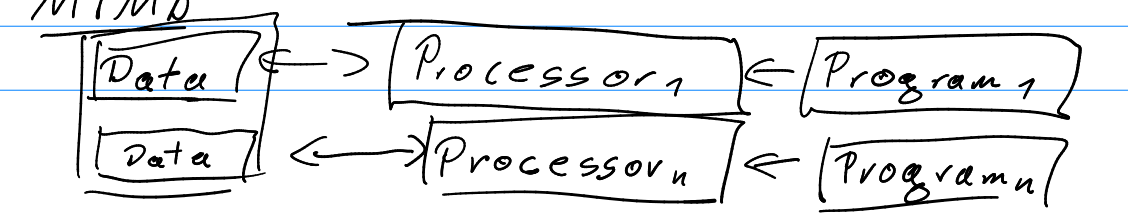
- Multiple Instruction Multiple Data (MIMD)
- Multiple data←>Multiple processors←Multiple Programs
- The data can access each other.
- Suitable for usage in Scientific computing, clusters etc.
Terminology
- Core:
- Arithmetic Unit + Control Unit, It conducts Float and Integer operations.
- CPU:
- Main processing Unit with several cores caches (these days.)
- Cache:
- Fast Indexed Memory that keeps copies of data from the main memory.
- RAM:
- Random access memory. Main access memory of the computer.
- Bus
- Data Transfer system. (E.g transfers data between RAM and CPU)
- Typically consisting of several lines. Note: A USB has a single line.
- Bus-width
- Number of parallel data lines in a Bus.
- Band-width
- Data throughput of a bus or network in Bytes/s
- Latency:
- Response time of bus or network or time between a query and start of an answer.
- Processing node
- Unit of one or more CPU’s with shared memory.
- Cluster
- Combination of several compute nodes.
- Computing Power
- Maximum floating point operations per second (FLOPS) (Arithmetic)
- Modern Computers can merge addition and multiplication
- Thread
- Independently executed sequences of Instructions.
- Process/Task
- Instance of an application with at least one thread.
- UMA-Machine: Uniform Memory Access - it takes the same to access any location in the memory.
- NUMA-Machine: non-UMA.
- ccNUMA: cache coherent NUMA - data in cache is kept valid when accessed by different cases. however this has an overhead.
- ncNUMA: non-cache coherent NUMA
SIMD Work Flow
- Check lecture notes for diagram
- In SIMD, threads have independent data but the same instructions.
MIMD Work Flow
- Threads with independent data and instructions.