MPI_Init
MPI_Init initializes the MPI environment. It must be called before any other MPI function. It defines the “Communicator” MPI_COMM_WORLD.
 Syntax
Syntax
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv)
where argc and argv are the command-line arguments.
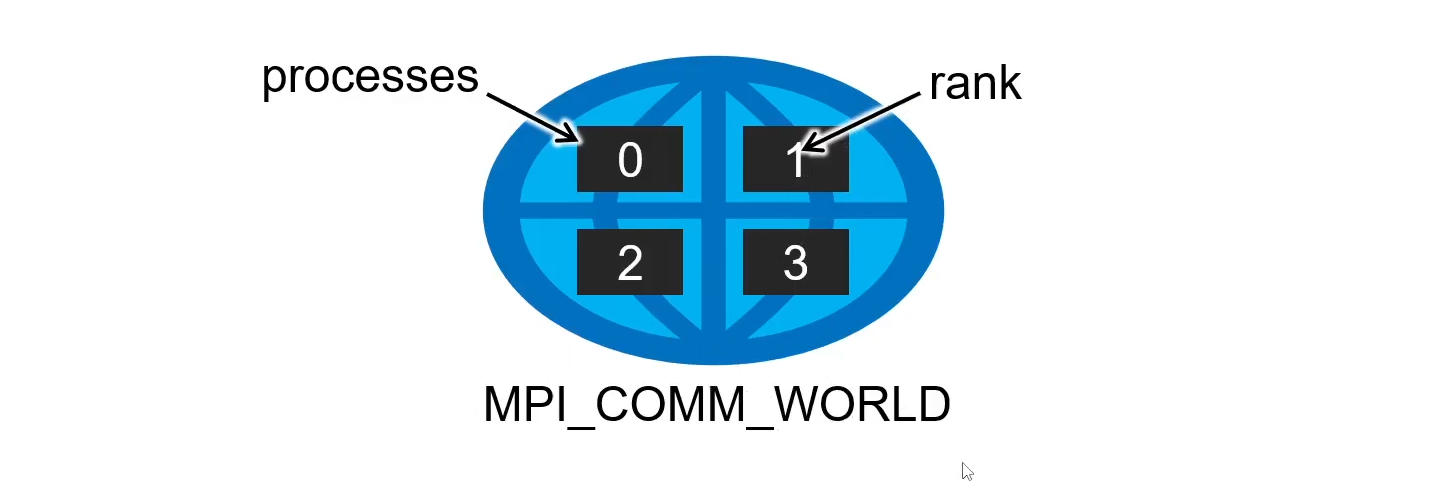
MPI_COMM_WORLD
MPI_COMM_WORLD is a predefined communicator that includes all the processes in the MPI program. It is used when you need to communicate among all processes.
Usage
MPI_COMM_WORLD is used as a parameter in various MPI functions to indicate that the function should operate on all processes in the MPI program.
Example
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &world_rank);
MPI_Comm_size
MPI_Comm_size determines the size of the group associated with a communicator. It returns the total number of processes in the communicator.
Syntax
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_Comm comm, int *size)
where comm is the communicator (e.g., MPI_COMM_WORLD) and size is the variable to store the number of processes.
MPI_Comm_rank
MPI_Comm_rank determines the rank of the calling process within the communicator. It returns the rank (ID) of the process.
Syntax
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_Comm comm, int *rank)
where comm is the communicator (e.g., MPI_COMM_WORLD) and rank is the variable to store the rank of the process.
MPI_Send
MPI_Send performs a standard-mode blocking send (the operation is complete only when the send buffer has been completely copied or the receiver has received the message). It sends data from one process to another.
Syntax
MPI_Send(const void *buf, int count, MPI_Datatype datatype, int dest, int tag, MPI_Comm comm)where
bufis the data buffercountis the number of elementsdatatypeis the type of elementsdestis the destination ranktagis an integer “label” for the messagecommis the communicator (usuallyMPI_COMM_WORLD)
Mnemonic: Don't Call; Dial Directly To ConnectMPI_Recv
MPI_Recv performs a standard-mode blocking receive. It receives data sent by another process.
Syntax
MPI_Recv(void *buf, int count, MPI_Datatype datatype, int source, int tag, MPI_Comm comm, MPI_Status *status)` where,
bufis the data buffercountis the number of elementsdatatypeis the type of elementssourceis the rank of the source processtagis an integer “label” for the messagecommis the communicator (usuallyMPI_COMM_WORLD)statusstatus object
Mnemonic: Don't Call; Dial Directly To Connect SoonMPI_Reduce
MPI_Reducecombines values from all processes and delivers the result to the specified root process.
Syntax
MPI_Reduce(&sendbuf, &recvbuf, count, datatype, op, root, comm);
where,
sendbuf: Address of the send buffer (input from each process).recvbuf: Address of the receive buffer (where the result will be stored on the root process).count: Number of elements in the buffer.datatype: Data type of the elements in the buffer (e.g.,MPI_DOUBLE).op: Operation to be applied (e.g.,MPI_SUMfor summation,MPI_MAXetc)root: Rank of the root process which will receive the result.comm: Communicator (e.g.,MPI_COMM_WORLD).
Mnemonic: Some Really Cool Dogs Only Run CirclesMPI_Bcast
MPI_Bcast Broadcasts a message from the process with rank “root” to all other processes of the communicator.
Syntax
MPI_Bcast( void *buffer, int count, MPI_Datatype datatype, int root,MPI_Comm comm )where,
buffer: Address of the buffer. This is the data that will be sent from the root process and received by all other processes.count: Number of elements in the buffer. This specifies how many elements of the specified datatype are being broadcast.datatype: Data type of the elements in the buffer (e.g.,MPI_DOUBLE,MPI_INT). This tells MPI the type of data it is dealing with.root: Rank of the root process which will send the data. The root process is where the data originates.comm: Communicator (e.g.,MPI_COMM_WORLD). This defines the group of processes involved in the broadcast operation.
Mnemonic: Brown Cookies Dream Round CookiesMPI_Finalize
MPI_Finalize terminates the MPI environment. It must be called after all other MPI functions.
Syntax
MPI_Finalize()
No arguments are required.