Mathematical Definition for a single prediction
1. Bayesian Predictive Distribution
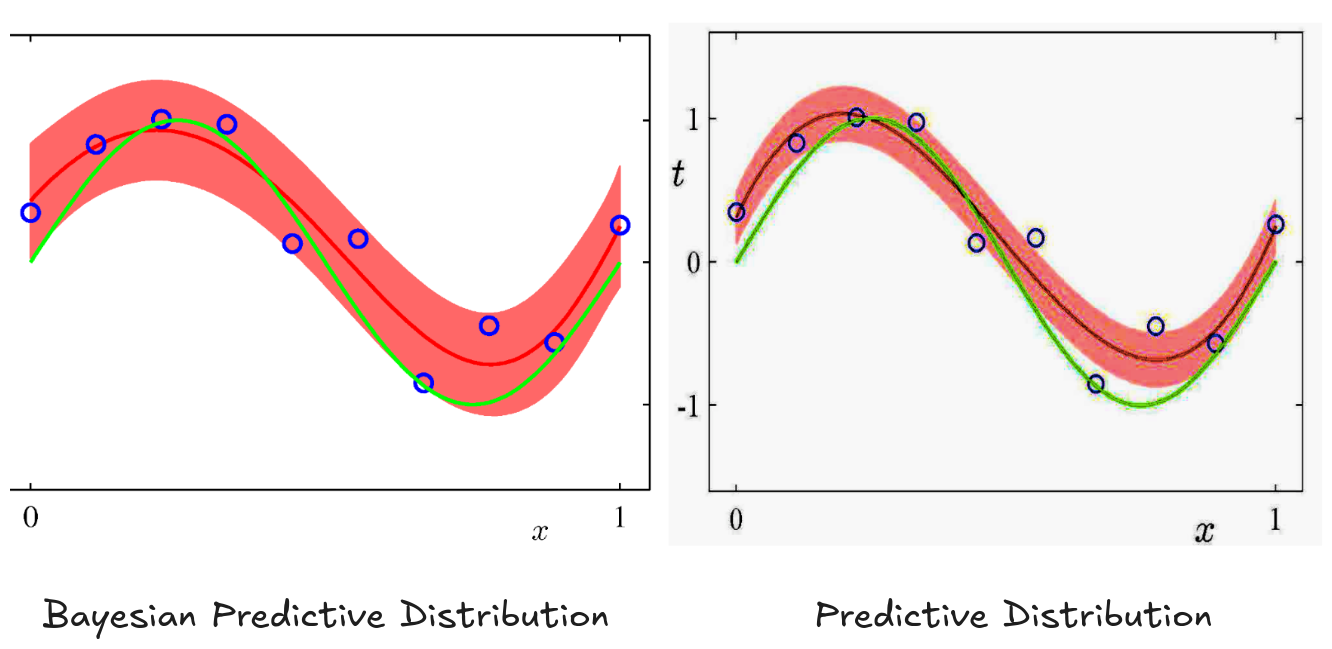
The Bayesian approach1(left plot) shows wider uncertainty bands because it accounts for parameter uncertainty on top of data noise. The uncertainty also varies spatially - being larger where there’s less data.
- Data-dependent mean:
- Input-dependent variance:
Note: The weight is not explicitly included in the parameters on the LHS of the Bayesian predictive distribution because it has been integrated out.
2. Predictive Distribution (Maximum Likelihood)
The Predictive Distribution uses a single “best” set of parameters found in the data.
- Fixed mean:
- Fixed variance: (constant for all inputs)
Summary of key differences
Predictive Distribution (Maximum Likelihood):
- Uses fixed parameters and (point estimates)
- Uncertainty comes only from data noise (aleatoric uncertainty)
- Constant variance across all inputs
Bayesian Predictive Distribution:
- Integrates over all possible parameters weighted by their posterior probability
- Uncertainty comes from both data noise AND parameter uncertainty (aleatoric + epistemic)
- Input-dependent variance - uncertainty varies with location
Footnotes
-
Help with the notation: is the probability distribution of a new, unseen output , conditioned on the new input and all the evidence from the training data, and . ↩