Definition
The equal error rate (EER) is defined as the point on a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve where the false acceptance rate (FAR) equals the false rejection rate (FRR).
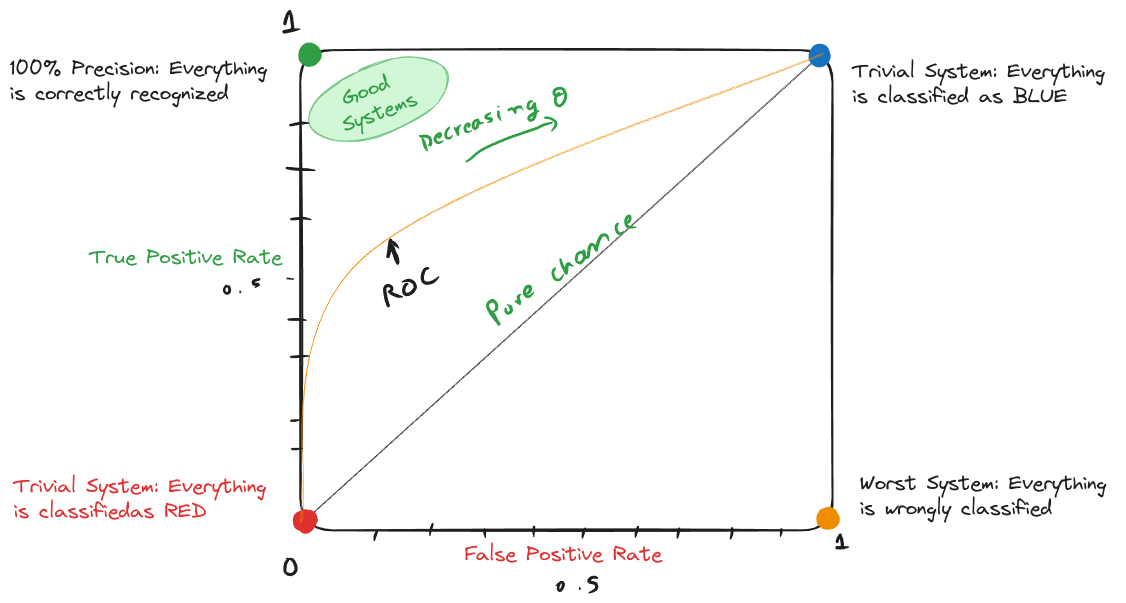
Operating to the RIGHT of EER (higher FPR, lower TPR):
- Medical diagnosis where missing a disease is worse than a false alarm
- Security pre-screening where not detecting a threat is more serious than unnecessary secondary checks
Operating to the LEFT of EER (lower FPR, higher TPR):
- Legal evidence where false accusations must be minimized
- Spam filtering where blocking legitimate emails is worse than letting some spam through